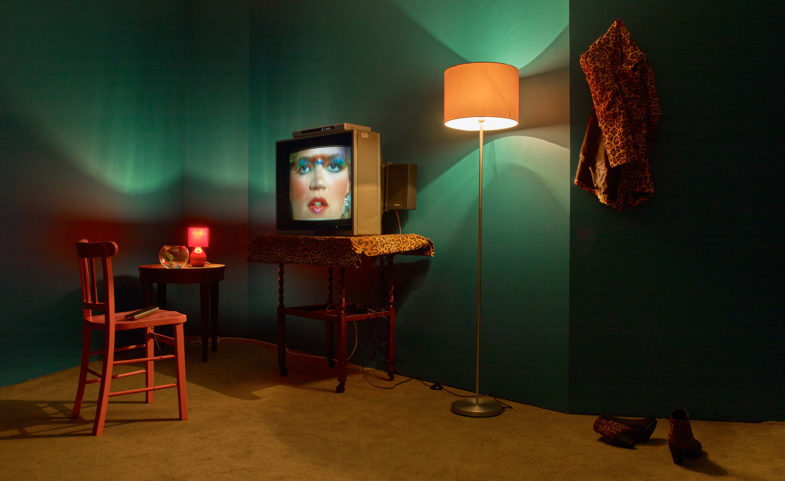
Tech-tonic: ‘Electronic Superhighway’
Tech-tonic: ‘Electronic Superhighway’ charts the shifting landscape of computer-art
When you think of Internet-based art, your mind might jump to the cutting edge. Although the hyper-modern aspects of multimedia art are displayed in the Whitechapel Gallery’s first show of the year, the emphasis is firmly on the medium’s rich and rebellious history.
‘Electronic Superhighway’ takes its name from one of its contributors – South Korean video artist Nam June Paik, who coined the term in 1977. In Paik’s Internet Dream – a major video-wall installation of 52 monitors displaying electronically-processed images – blurred, garish colours have a hypnotic effect, showing his early awareness of society’s move towards information saturation.
This abundance of data, ironically, could occur in such an ambitious, extensive exhibition. The dizzying array of computer screens, installations and radio static that greets gallery-goers is deliberately overwhelming. To prevent complete over-stimulation, ‘Electronic Superhighway’ is dispersed over two floors and three different gallery spaces, working backwards chronologically from the present day.
On the ground floor, web art is represented by Amalia Ulman’s Excellences Perfections Instagram, a four-month documentary series which examines the influence of social media on attitudes towards the female form. The theme of online identity (or lack thereof) is continued by Douglas Coupland’s famously obscured Deep Face – a comment on Facebook’s involuntary facial recognition technology.
As visitors make their way up stairs, they journey back to the 1990s. At the top of the staircase, Aristakh Chernyshev’s custom LED panel eternally loops the word ‘Loading’ around in a frustrating circle. This signifies that although visitors are moving upwards, they are regressing into a time when information was not demanded or expected instantaneously.
The second gallery space concentrates on the explosion of the Internet, which brought with it an explosion of browser-based works. Ann Hircsh’s Twelve (2013) and Martine Neddam’s Mouchette.org (1996) present interactive narratives about vulnerable teenage girl-users. In the latter, fluffy pink pens sit alongside vulgar images on a tablet, with no writing paper in sight.
In the final space, the tone shifts again. Here, the exhibition’s pervading sense of foreboding is mingled with some light optimism – the works look forward to a bright-screened future. The 60s and 70s feature boundary-testing artists who pushed early technology to its creative limits. Highlights include the intricate, plotter-based algorithmic work by Manfred Mohr, and the early digital-media design of Frieder Nake.
‘Electronic Superhighway’ ends at the beginning, with memorabilia from Experiments in Art and Technology (E.A.T) – a series of events that took place in 1960s New York, which showcased artists like John Cage and Robert Rauschenberg. And what better way to end an exhibition about screen-based works, than with a good old-fashioned cabinet of physical artefacts.